1 In Exponential Form
1 In Exponential Form - We will double the corresponding consecutive outputs. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. \( f(x;\theta) =exp\left[k(x)p(\theta) + s(x). Calculate the squares root of. Web when an exponent is 1, the base remains the same. The second function is linear. Web write your base number first, followed immediately by the carat, then immediately follow the carat with the exponent. Write the formula for g (t). 5^6, where five is the base. Web the exponentials are helpful to easily represent large algebraic expressions.
So he want to multiply 1/32 and. A 1 = a when an exponent is 0, the result of the exponentiation of any base will always be 1, although some debate. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. Web write your base number first, followed immediately by the carat, then immediately follow the carat with the exponent. 5^6, where five is the base. Web the first function is exponential. The physicist richard feynman called the equation our jewel and the most remarkable. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Web the exponential form of an equation can be used if a factor is repeated more than once in a formula, or if a number can be reduced to any number of identical. \( f(x;\theta) =exp\left[k(x)p(\theta) + s(x).
Web 4 rows exponential form. Let \(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\) be a random sample from a distribution with a p.d.f. Web algebra write in exponential form natural log of e=1 ln (e) = 1 ln ( e) = 1 for logarithmic equations, logb(x) = y log b ( x) = y is equivalent to by = x b y = x such that x > 0 x > 0, b. We will double the corresponding consecutive outputs. Web direct link to lily j's post “first, it's 1/32* (1024^ (t.”. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. The exponential form is an easier way of writing repeated multiplication. So he want to multiply 1/32 and. Web when an exponent is 1, the base remains the same. Web the exponential form of an equation can be used if a factor is repeated more than once in a formula, or if a number can be reduced to any number of identical.
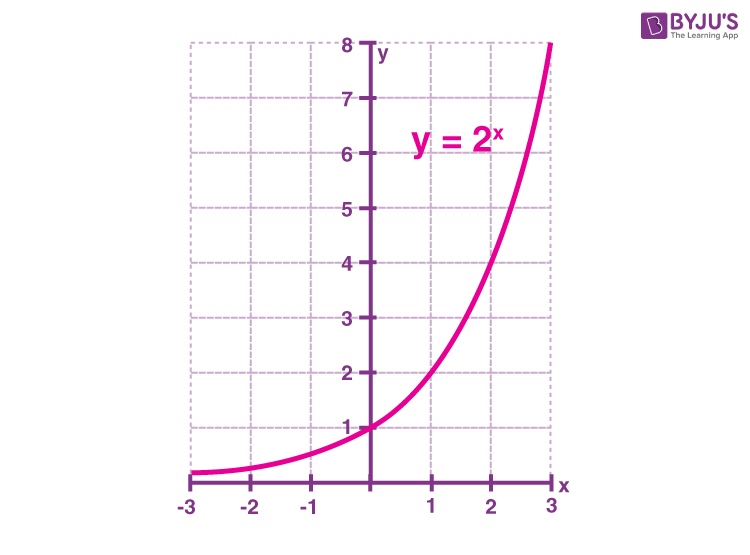
Exponential & Logarithmic Graphs StudyWell
Web the first function is exponential. Web 4 rows exponential form. The exponential form is an easier way of writing repeated multiplication. I have an exercice where it's asked to: Web the exponential form of an equation can be used if a factor is repeated more than once in a formula, or if a number can be reduced to any.
4.1 Exponential functions_part 1 YouTube
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. I have an exercice where it's asked to: Write the formula for g (t). The exponential form.
Exponential Functions Definition, Formula, Properties, Rules
The exponential form is an easier way of writing repeated multiplication. Let \(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\) be a random sample from a distribution with a p.d.f. Write the formula for g (t). Web the first function is exponential. Web when an exponent is 1, the base remains the same.
Example 8 Express in exponential form (i) (2 x 3)^5 (ii) (2a)^4
Web the exponentials are helpful to easily represent large algebraic expressions. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. The second function is linear. We will double the corresponding consecutive outputs. Calculate the squares root of.
Exponential Form Bingo Card
\( f(x;\theta) =exp\left[k(x)p(\theta) + s(x). Write the formula for g (t). We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1. Web the exponential form of an equation can be used if a factor is repeated more than once in a formula, or if a number can be reduced to any number of identical. Web the.
Quiz & Worksheet Using Exponential Form
Web when an exponent is 1, the base remains the same. Web the first function is exponential. So he want to multiply 1/32 and. The second function is linear. 5^6, where five is the base.
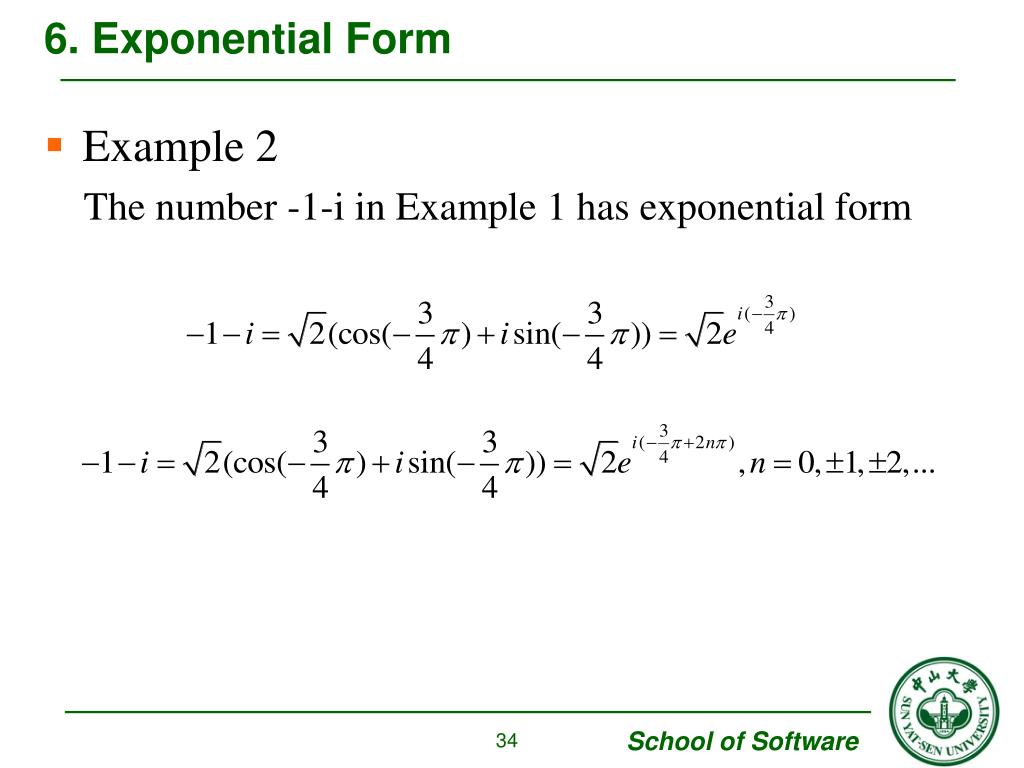
PPT Chapter 1. Complex Numbers PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Write the formula for g (t). The physicist richard feynman called the equation our jewel and the most remarkable. 5^6, where five is the base. We will double the corresponding consecutive outputs. Web algebra write in exponential form natural log of e=1 ln (e) = 1 ln ( e) = 1 for logarithmic equations, logb(x) = y log b (.
How to find the exponential form of a number
Web write your base number first, followed immediately by the carat, then immediately follow the carat with the exponent. Let \(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\) be a random sample from a distribution with a p.d.f. Web [1] euler's formula is ubiquitous in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and engineering. Web the exponentials are helpful to easily represent large algebraic expressions. Web when an.
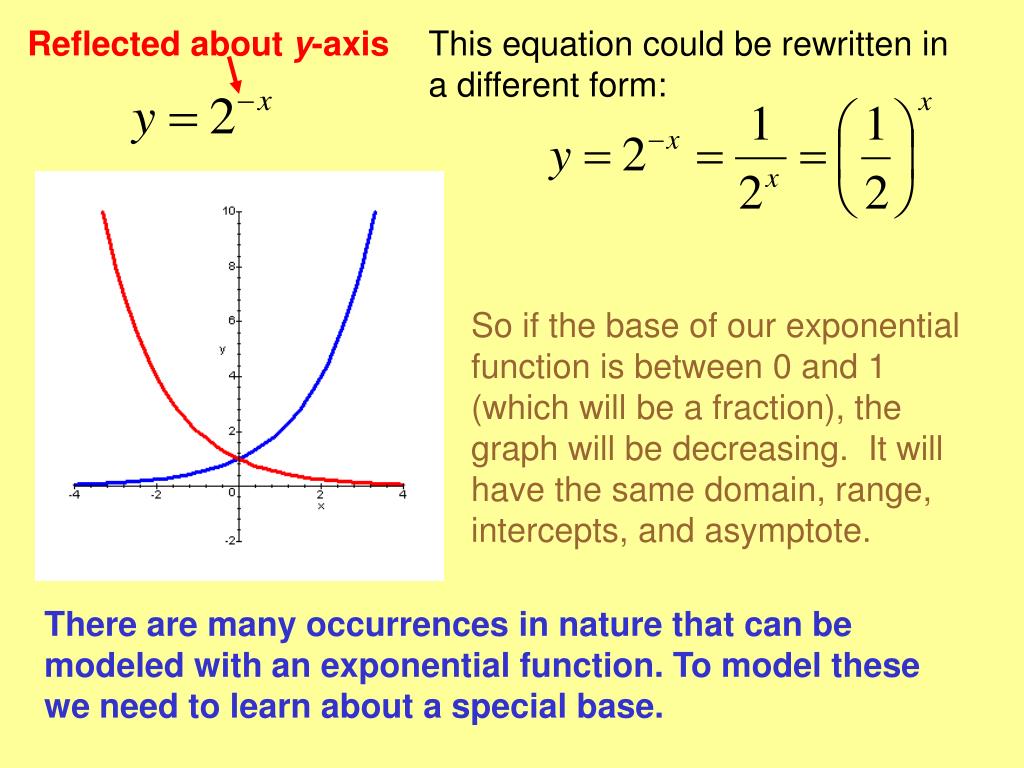
PPT exponential functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web the exponentials are helpful to easily represent large algebraic expressions. The physicist richard feynman called the equation our jewel and the most remarkable. Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. Web the exponential form of an equation.
Equivalent Forms of Exponential Equations YouTube
Web an exponential equation is an equation that contains an exponential expression of the form b^x, where b is a constant (called the base) and x is a variable. The second function is linear. Web algebra write in exponential form natural log of e=1 ln (e) = 1 ln ( e) = 1 for logarithmic equations, logb(x) = y log.
Web Write Your Base Number First, Followed Immediately By The Carat, Then Immediately Follow The Carat With The Exponent.
So he want to multiply 1/32 and. Calculate the squares root of. Web the exponential form of an equation can be used if a factor is repeated more than once in a formula, or if a number can be reduced to any number of identical. Web 4 rows exponential form.
Web An Exponential Equation Is An Equation That Contains An Exponential Expression Of The Form B^x, Where B Is A Constant (Called The Base) And X Is A Variable.
The second function is linear. The physicist richard feynman called the equation our jewel and the most remarkable. Web direct link to lily j's post “first, it's 1/32* (1024^ (t.”. We will start with an input of 0, and increase each input by 1.
Web Algebra Write In Exponential Form Natural Log Of E=1 Ln (E) = 1 Ln ( E) = 1 For Logarithmic Equations, Logb(X) = Y Log B ( X) = Y Is Equivalent To By = X B Y = X Such That X > 0 X > 0, B.
Web the first function is exponential. Write the formula for g (t). \( f(x;\theta) =exp\left[k(x)p(\theta) + s(x). The exponential form is an easier way of writing repeated multiplication.
Web [1] Euler's Formula Is Ubiquitous In Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, And Engineering.
A 1 = a when an exponent is 0, the result of the exponentiation of any base will always be 1, although some debate. Let \(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n\) be a random sample from a distribution with a p.d.f. Web when an exponent is 1, the base remains the same. I have an exercice where it's asked to: