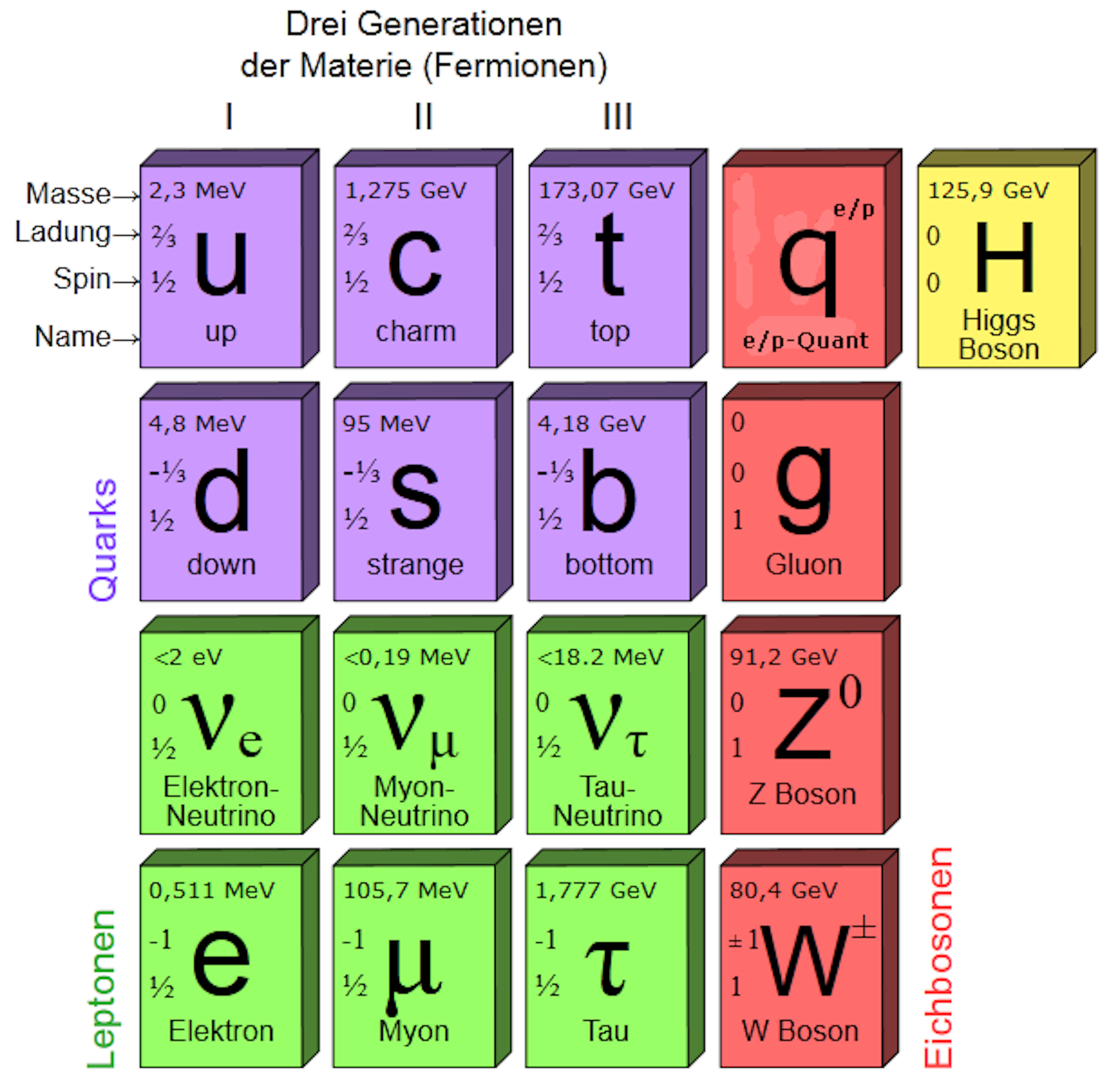
Form Particle Physics
Form Particle Physics - Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume,. Web a large number of subatomic particles exist in nature. Web particle physics physicists see ‘strange matter’ form inside atomic nuclei new research attempts to discern how bizarre particles of strange matter form in the. Kg m s are a natural choice for “everyday” objects e.g. The property of spin and participation in the four fundamental. Its starting point is the. Web the science of particle physics surged forward with the invention of particle accelerators that could accelerate protons or electrons to high energies and smash them into nuclei. These particles can be classified in two ways: Web in elementary particle physics and mathematical physics, in particular in effective field theory, a form factor is a function that encapsulates the properties of a certain. Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing with the constitution, properties, and interactions of elementary particles especially as.
Thomson michaelmas 2009 5 preliminaries: M(prescott) ~ 250 kg • not very natural in. Web the science of particle physics surged forward with the invention of particle accelerators that could accelerate protons or electrons to high energies and smash them into nuclei. These particles can be classified in two ways: Spin is a convenient label for a measurable quality and not a description of reality. Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume,. Web physics, science that deals with the structure of matter and the interactions between the fundamental constituents of the observable universe. Web the typical model of particle physics is a theory associated with the electromagnetic, nuclear interactions and also organizing the subatomic particles. Web 11 rows list of particles this is a list of known and hypothesized particles. You will learn about the fundamental components of.
Broadly defined, particle physics aims to answer the fundamental questions of the nature of mass, energy, and matter, and their relations to the. Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume,. Web the typical model of particle physics is a theory associated with the electromagnetic, nuclear interactions and also organizing the subatomic particles. Web the science of particle physics surged forward with the invention of particle accelerators that could accelerate protons or electrons to high energies and smash them into nuclei. Its starting point is the. Web particle physics is best described with mathematics. M(prescott) ~ 250 kg • not very natural in. Web the standard model of elementary particle physics describes with amazing parsimony (only 19 parameters!) all known interactions over the scales that. Web developed by the dutch particle physicist jos vermaseren, form is a key part of the infrastructure of particle physics, necessary for the hardest. Web this free course, particle physics, will give you an overview of current concepts and theories in the field.
The Standard Model of Particle Physics The Absolutely Amazing Theory
You will learn about the fundamental components of. Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing with the constitution, properties, and interactions of elementary particles especially as. These particles can be classified in two ways: Web developed by the dutch particle physicist jos vermaseren, form is a key part of the infrastructure of particle physics, necessary.
The particle physics of you symmetry magazine
These particles can be classified in two ways: Web in elementary particle physics and mathematical physics, in particular in effective field theory, a form factor is a function that encapsulates the properties of a certain. Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or.
Science Visualized • STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Graphical...
Spin is a convenient label for a measurable quality and not a description of reality. Web the standard model of elementary particle physics describes with amazing parsimony (only 19 parameters!) all known interactions over the scales that. You will learn about the fundamental components of. Broadly defined, particle physics aims to answer the fundamental questions of the nature of mass,.
Diagram of the Standard Model of particle physics. 12 fundamental
Web particle physics protons, neutrons, pions, and other hadrons one of the most significant branches of contemporary physics is the study of the fundamental subatomic. Web physics, science that deals with the structure of matter and the interactions between the fundamental constituents of the observable universe. Spin is a convenient label for a measurable quality and not a description of.
Particle Physics Science Woke
Elementary particles elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; Web developed by the dutch particle physicist jos vermaseren, form is a key part of the infrastructure of particle physics, necessary for the hardest. Web physics, science that deals with the structure of matter and the interactions between the fundamental constituents of the observable universe. Web in the physical.
The Fundamentals of Elementary Particle Physics
Its starting point is the. M(prescott) ~ 250 kg • not very natural in. Web the standard model of elementary particle physics describes with amazing parsimony (only 19 parameters!) all known interactions over the scales that. Web this free course, particle physics, will give you an overview of current concepts and theories in the field. Kg m s are a.
Particle physics discovery raises hope for a theory of everything
Spin is a convenient label for a measurable quality and not a description of reality. Its starting point is the. Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume,. Web particle physics protons, neutrons, pions, and other hadrons one.
The Particle Physics of You Department of Energy
Web the science of particle physics surged forward with the invention of particle accelerators that could accelerate protons or electrons to high energies and smash them into nuclei. The property of spin and participation in the four fundamental. Web a large number of subatomic particles exist in nature. Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing.
Ultracold Quantum Particles Break Classical Symmetry
Its starting point is the. Web in elementary particle physics and mathematical physics, in particular in effective field theory, a form factor is a function that encapsulates the properties of a certain. Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing with the constitution, properties, and interactions of elementary particles especially as. You will learn about the.
Quantum entanglement
Web the standard model of elementary particle physics describes with amazing parsimony (only 19 parameters!) all known interactions over the scales that. Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing with the constitution, properties, and interactions of elementary particles especially as. Web a large number of subatomic particles exist in nature. Web 11 rows list of.
Broadly Defined, Particle Physics Aims To Answer The Fundamental Questions Of The Nature Of Mass, Energy, And Matter, And Their Relations To The.
Web in the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume,. Web physics, science that deals with the structure of matter and the interactions between the fundamental constituents of the observable universe. You will learn about the fundamental components of. Web developed by the dutch particle physicist jos vermaseren, form is a key part of the infrastructure of particle physics, necessary for the hardest.
Web In Elementary Particle Physics And Mathematical Physics, In Particular In Effective Field Theory, A Form Factor Is A Function That Encapsulates The Properties Of A Certain.
Web the meaning of particle physics is a branch of physics dealing with the constitution, properties, and interactions of elementary particles especially as. Web particle physics physicists see ‘strange matter’ form inside atomic nuclei new research attempts to discern how bizarre particles of strange matter form in the. Spin is a convenient label for a measurable quality and not a description of reality. Web particle physics protons, neutrons, pions, and other hadrons one of the most significant branches of contemporary physics is the study of the fundamental subatomic.
These Particles Can Be Classified In Two Ways:
Elementary particles elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; Web the typical model of particle physics is a theory associated with the electromagnetic, nuclear interactions and also organizing the subatomic particles. Web a large number of subatomic particles exist in nature. Web particle physics is best described with mathematics.
M(Prescott) ~ 250 Kg • Not Very Natural In.
Its starting point is the. Web the science of particle physics surged forward with the invention of particle accelerators that could accelerate protons or electrons to high energies and smash them into nuclei. The property of spin and participation in the four fundamental. Web form factors of elementary particles scattering of electrons on nucleons and electron‐positron scattering in colliding‐beam experiments give a measure of the size.


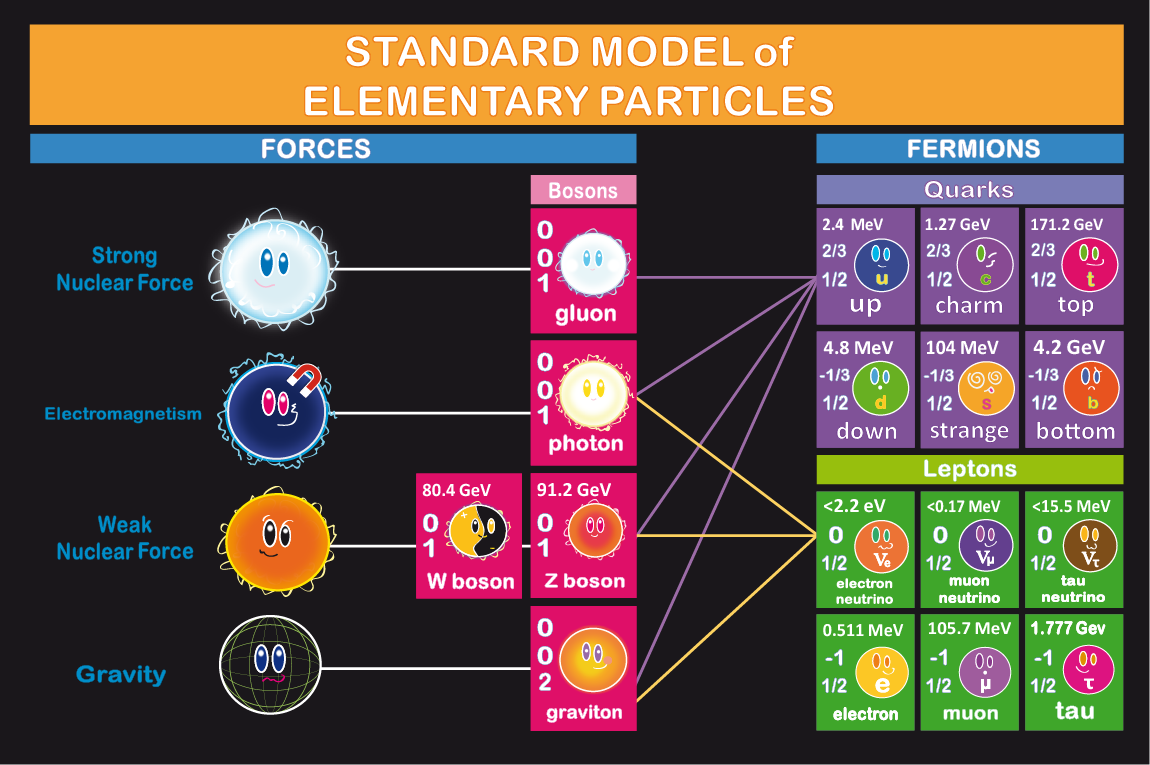


/GettyImages-475158089-57f676975f9b586c35f96dc5.jpg)