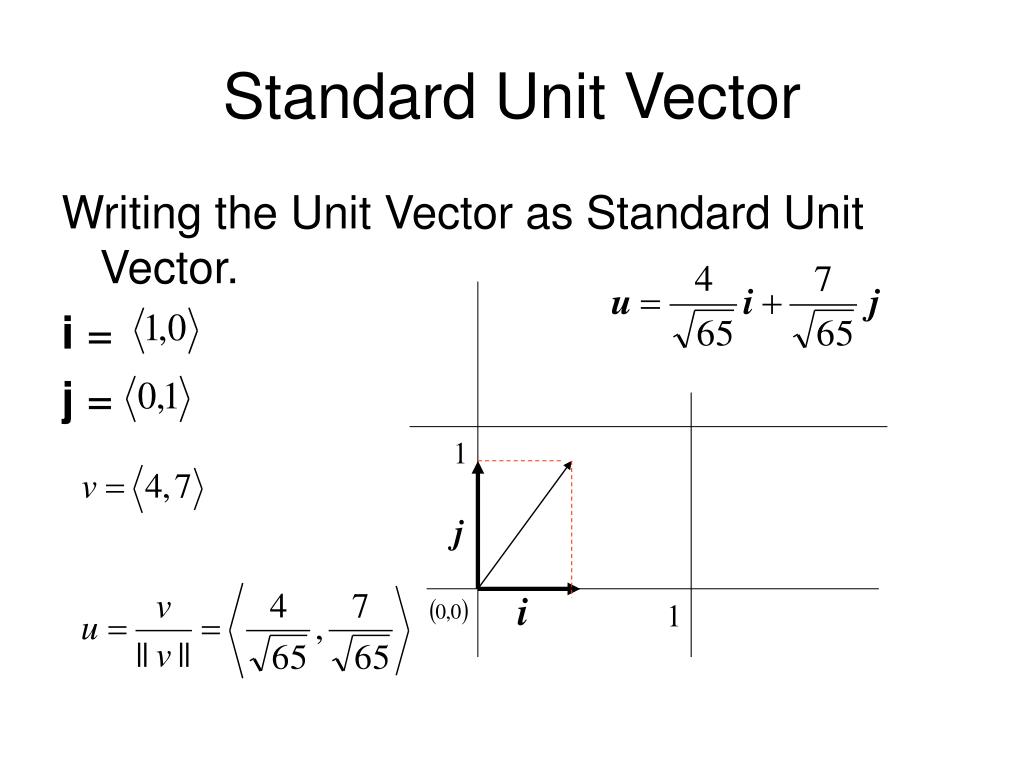
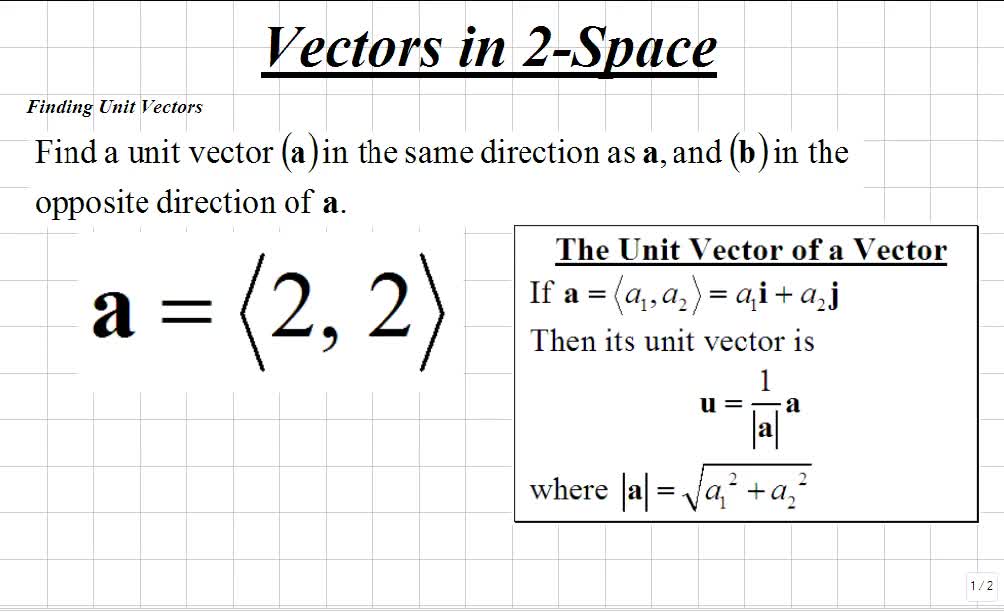
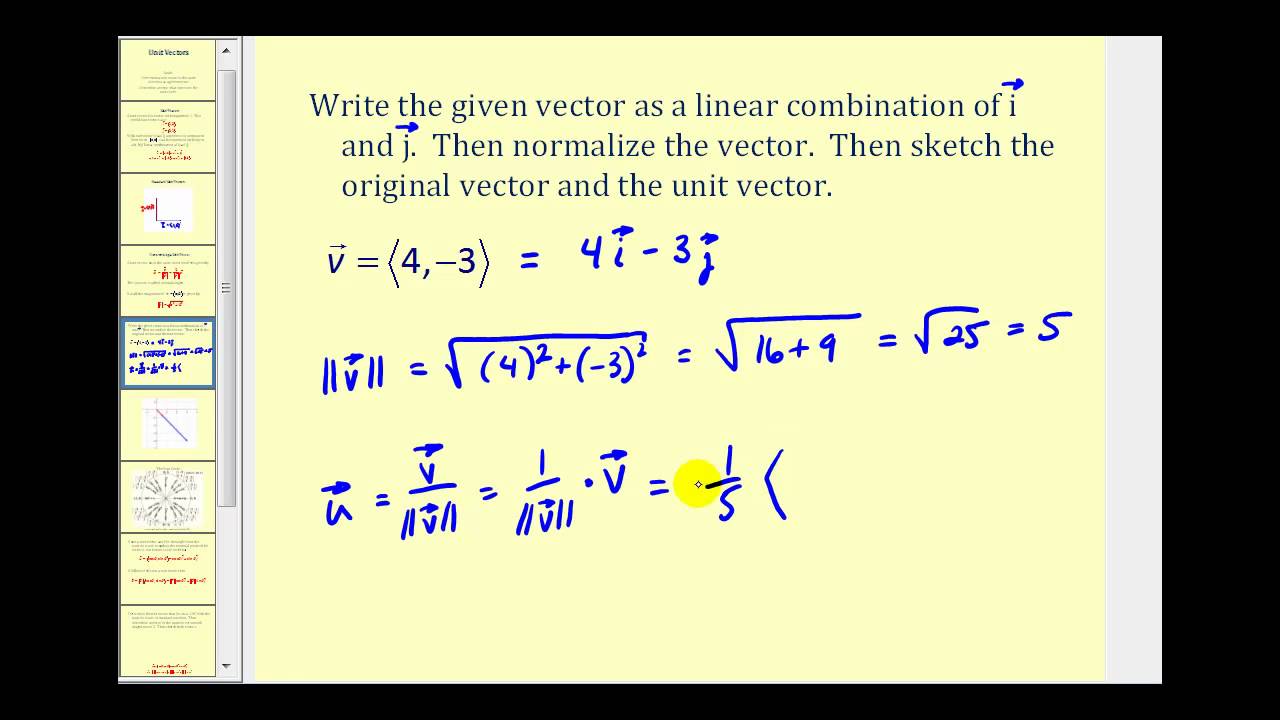
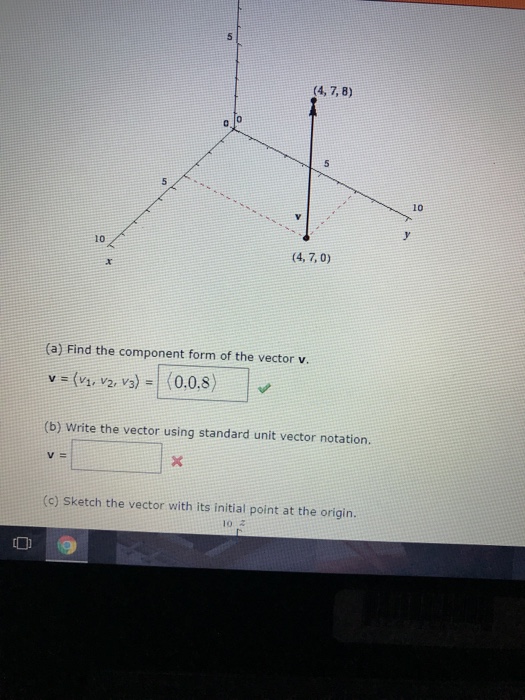
Standard Unit Vector Form
Standard Unit Vector Form - We need to find scalars a and b such that. I and j are the standard unit vectors in the x and y directions. (2.18) this procedure gives unit magnitude but preserves the radial direction of r. Web express a vector in component form. Web by definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors. Write your answer in either component vector. Web the unit normal vector formula is, n(x) =t′(x)/||t′(x)|| as directly compared to the formula for the unit tangent vector, when we consider the unit tangent vector as a. [2 4] =a[2 1]+b[ 2 −2] this amounts to solving a system of linear equations. However, an ordered orthonormal basis is not. Web standard unit vector form
We need to find scalars a and b such that. Web the unit vector is formed by taking the position vector r and dividing it by its magnitude: Find the vector difference a − b a − b and express it in. In other words, it is an ordered and orthonormal basis. (2.18) this procedure gives unit magnitude but preserves the radial direction of r. Web determine the vector sum a + b a + b and express it in both the component form and by using the standard unit vectors. Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k k multiplied by scalars a,b,c ∈ r a, b, c ∈ ℝ. Write your answer in either component vector. Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle. Web standard unit vector form
Web by definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors. Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle. Web we introduce standard unit vectors in \rr2, \rr3 and \rrn, and express a given vector as a linear combination of standard unit vectors. I and j are the standard unit vectors in the x and y directions. Find the component form of with initial point. Vectors vector intro for linear algebra real coordinate spaces adding vectors algebraically & graphically multiplying a vector by a scalar vector examples scalar. $i,j,k$ if you use that notation, or. Web the unit vector is formed by taking the position vector r and dividing it by its magnitude: However, an ordered orthonormal basis is not. Use the given magnitude and direction to find the vector v in standard position.
PPT 6.3 Vector in the Plane PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web see how to break vectors into x and y components, and how to use unit vector notation to label vectors in a way that represents them more efficiently and analytically, making it. In other words, it is an ordered and orthonormal basis. Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k.
Unit Vector at Collection of Unit Vector free for
Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k k multiplied by scalars a,b,c ∈ r a, b, c ∈ ℝ. Web express a vector in component form. Use the given magnitude and direction to find the vector v in standard position. Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit.
PPT Vectors PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6014278
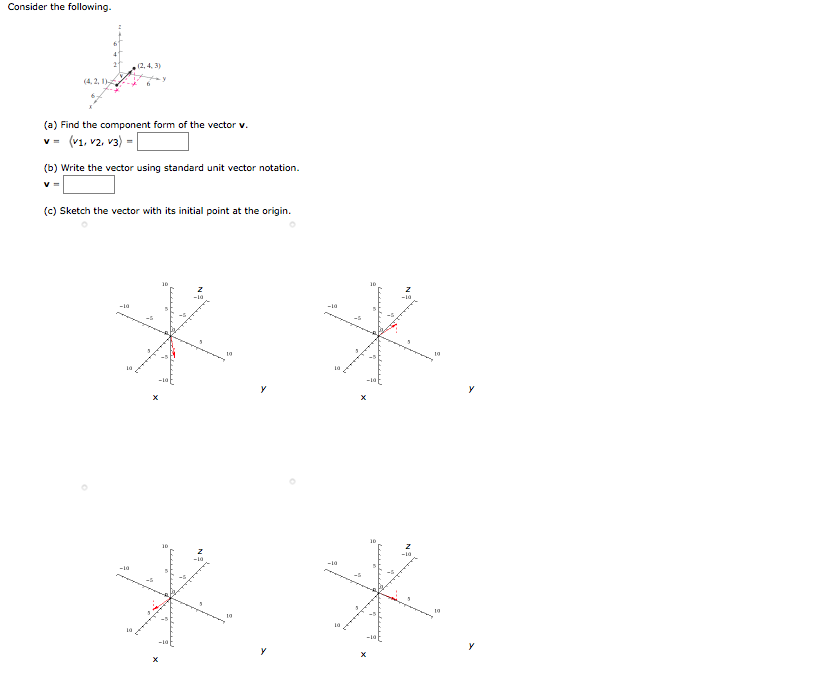
$i,j,k$ if you use that notation, or. (a) find the component form of the vector v, (b) write the vector using standard unit. (2.18) this procedure gives unit magnitude but preserves the radial direction of r. [2 4] =a[2 1]+b[ 2 −2] this amounts to solving a system of linear equations. Write your answer in either component vector.
The Unit Vector (2D) YouTube
Web the unit vector is formed by taking the position vector r and dividing it by its magnitude: Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle. Web by definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors. → p = ai + bj. $i,j,k$ if you use that notation, or.
Solved (4, 7, 8) 10 10 (4, 7,0) (a) Find the component form
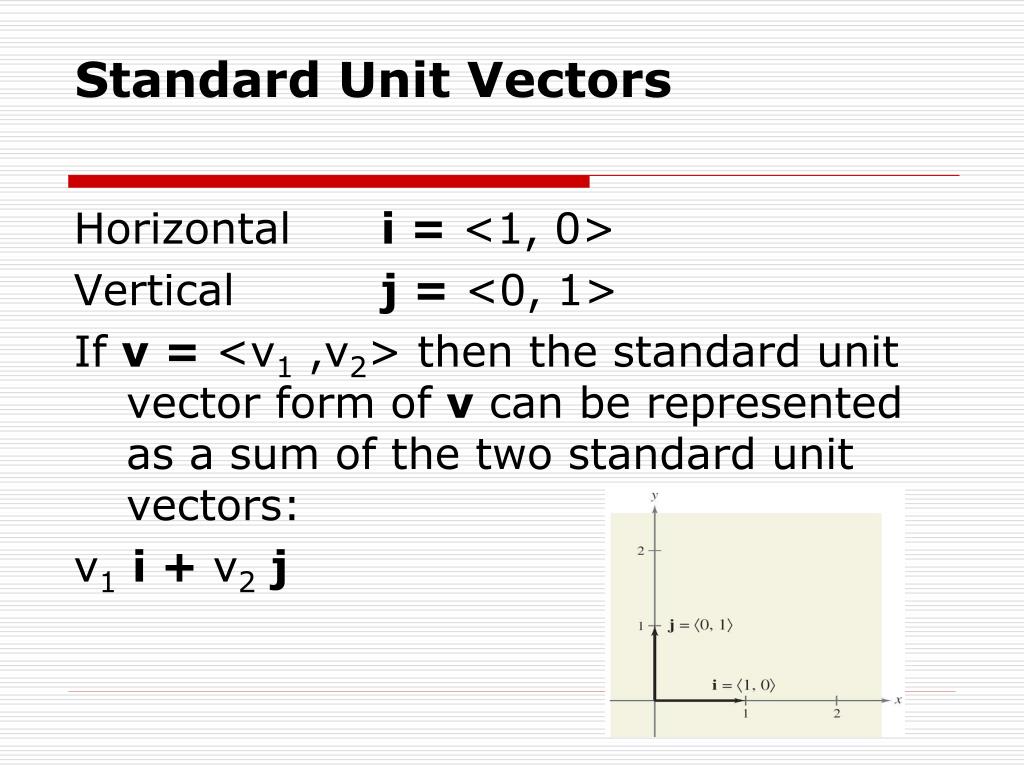
→ p = ai + bj. Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k k multiplied by scalars a,b,c ∈ r a, b, c ∈ ℝ. Web by definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors. Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf.
Solved Consider the followin 9 4.2.1 (a) Find the component
We need to find scalars a and b such that. Use the given magnitude and direction to find the vector v in standard position. Web interpret your results geometrically. (2.18) this procedure gives unit magnitude but preserves the radial direction of r. Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle.
PPT Vectors PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6014278
Web we introduce standard unit vectors in \rr2, \rr3 and \rrn, and express a given vector as a linear combination of standard unit vectors. Web the unit vector is formed by taking the position vector r and dividing it by its magnitude: Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle. Web the.
PPT Section 3.4 PowerPoint Presentation ID3943530
We need to find scalars a and b such that. Web the unit vector is formed by taking the position vector r and dividing it by its magnitude: (a) find the component form of the vector v, (b) write the vector using standard unit. $i,j,k$ if you use that notation, or. Magnitude & direction form of vectors.
Standard Unit Vectors YouTube
However, an ordered orthonormal basis is not. Write your answer in either component vector. Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k k multiplied by scalars a,b,c ∈ r a, b, c ∈ ℝ. Web express a vector in component form. Use the given magnitude and direction to find the vector.
Unit Vector at Collection of Unit Vector free for
(2.18) this procedure gives unit magnitude but preserves the radial direction of r. Use the given magnitude and direction to find the vector v in standard position. Write your answer in either component vector. Web see how to break vectors into x and y components, and how to use unit vector notation to label vectors in a way that represents.
However, An Ordered Orthonormal Basis Is Not.
Find the vector difference a − b a − b and express it in. [2 4] =a[2 1]+b[ 2 −2] this amounts to solving a system of linear equations. I and j are the standard unit vectors in the x and y directions. Write your answer in either component vector.
Web Unit Vectors Are Any Vector $U$ Where $\|U\| = 1$ The Standard Unit Vectors Are The Unit Vectors That Are Parallel To The Coordinate Axes.
Web we introduce standard unit vectors in \rr2, \rr3 and \rrn, and express a given vector as a linear combination of standard unit vectors. Vectors vector intro for linear algebra real coordinate spaces adding vectors algebraically & graphically multiplying a vector by a scalar vector examples scalar. Web see how to break vectors into x and y components, and how to use unit vector notation to label vectors in a way that represents them more efficiently and analytically, making it. Web determine the vector sum a + b a + b and express it in both the component form and by using the standard unit vectors.
Use The Given Magnitude And Direction To Find The Vector V In Standard Position.
Web this interactive shows the graphical relations between the unit vector ˆf and the unit circle. Web interpret your results geometrically. 2a+2b a−2b= 2 = 4. Web by definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors.
We Need To Find Scalars A And B Such That.
Find the component form of with initial point. (a) find the component form of the vector v, (b) write the vector using standard unit. Component form of vector representation is the sum of standard unit vector i i, j j, k k multiplied by scalars a,b,c ∈ r a, b, c ∈ ℝ. Web express a vector in component form.