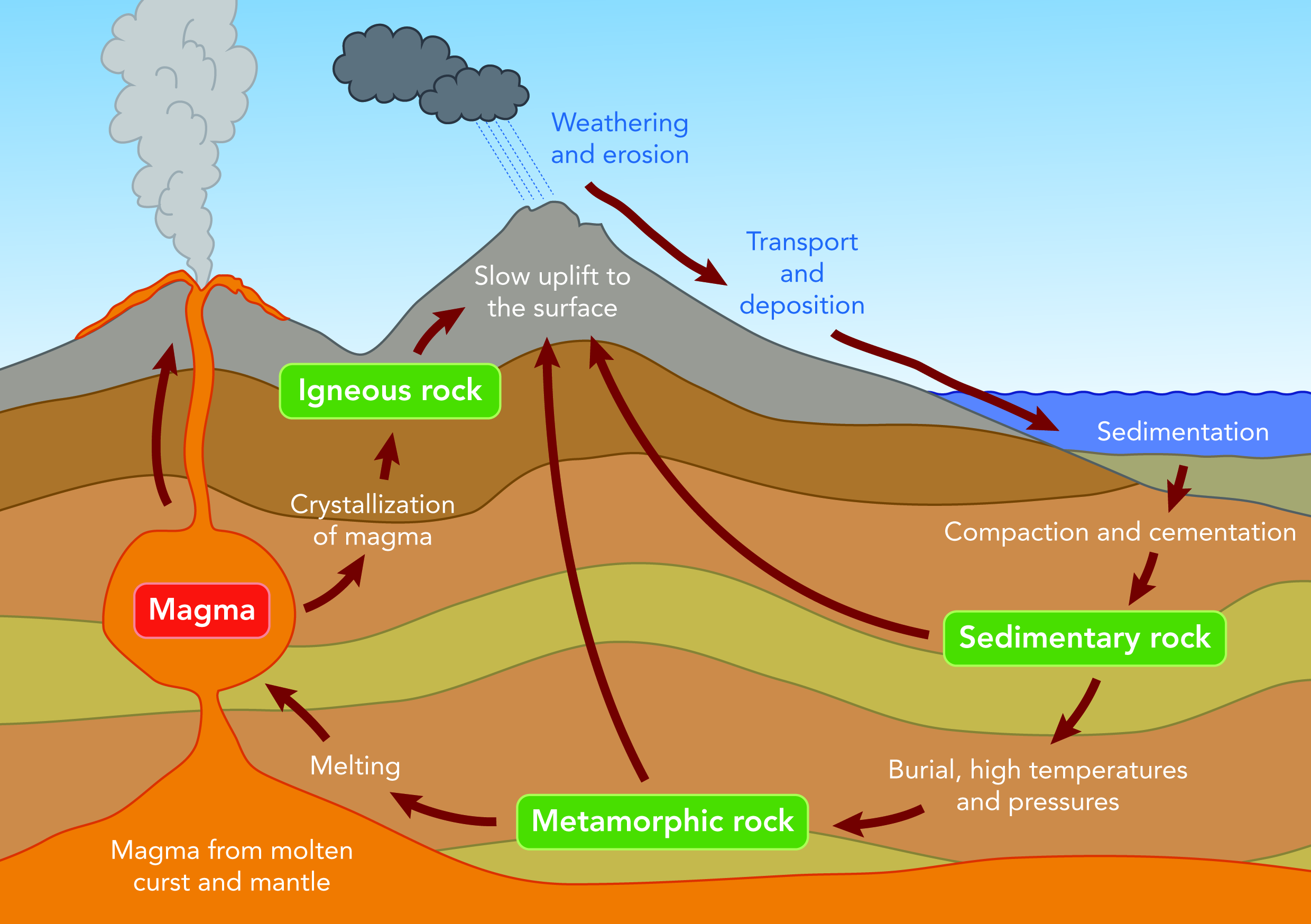
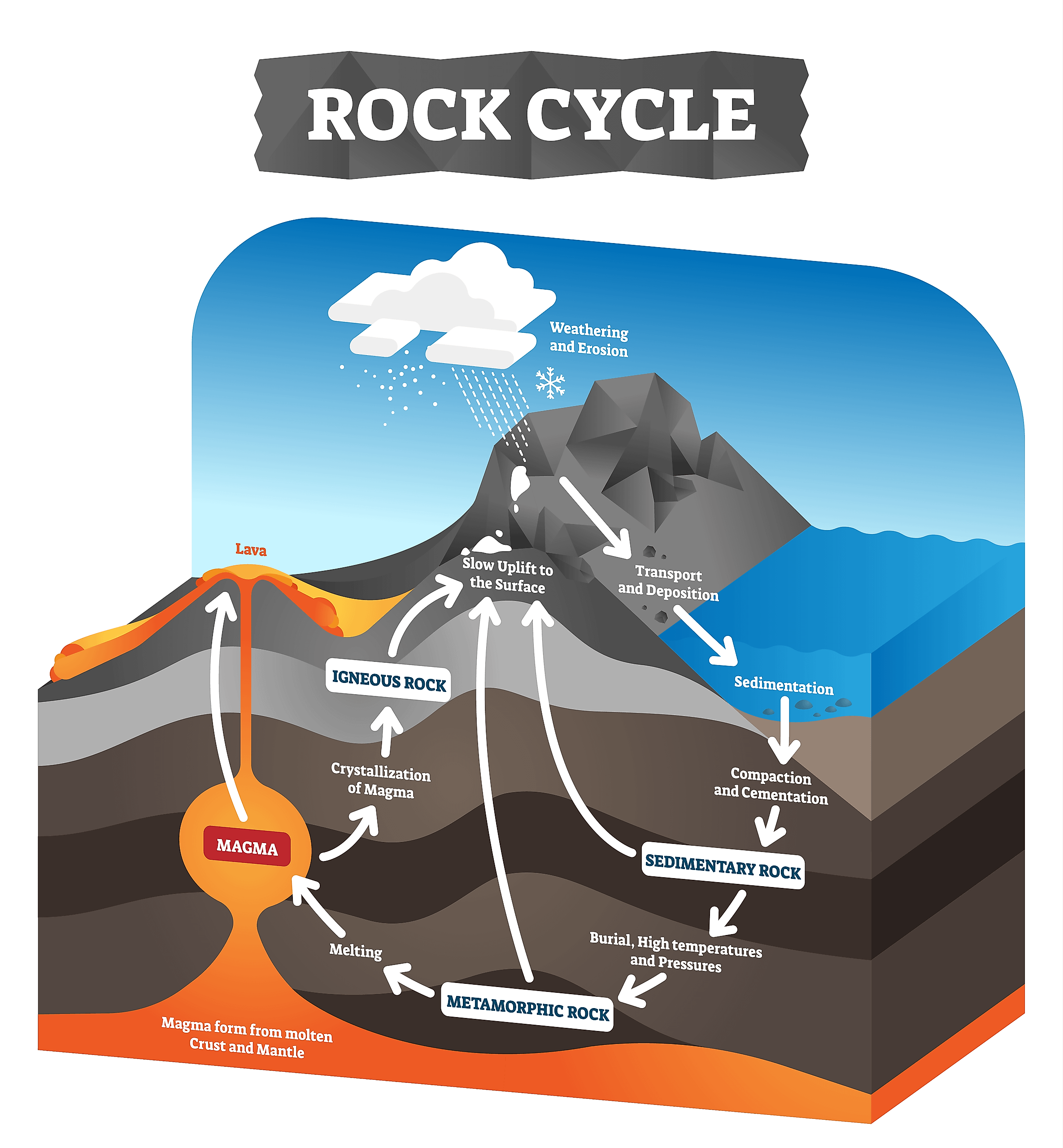
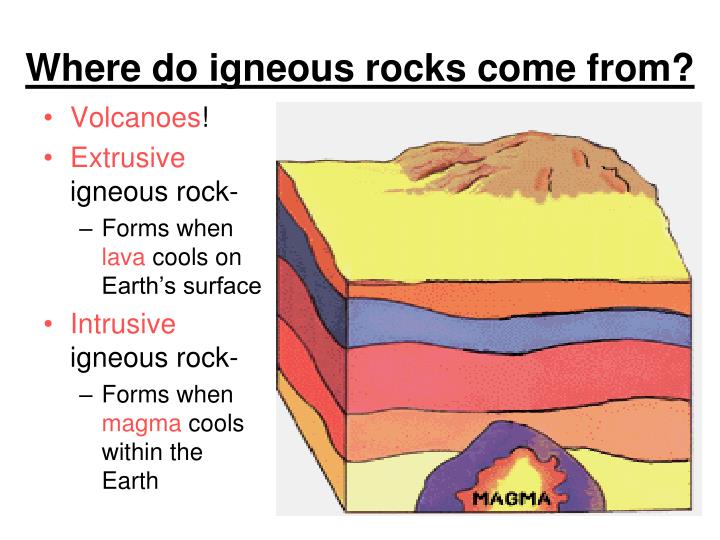
Where Do Extrusive Igneous Rocks Form
Where Do Extrusive Igneous Rocks Form - Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Basalt is rich in iron and magnesium and is mainly. Web extrusive igneous rocks. Web extrusive igneous rocks are formed by lava that cools at the earth’s surface. Specimens are black in color and weather to dark green or brown. These are igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary. Igneous rocks that form at earth's surface from rapidly cooling lava. Web extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently. Some cool so quickly that they form an amorphous glass. Web extrusive igneous rocks form when magma reaches the earth’s surface a volcano and cools quickly.
Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Basalt is rich in iron and magnesium and is mainly. Web quiz key points there are three types of rock found on earth. These rocks usually form from a volcano (called volcanic rocks.) cool much more. Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to earth's surface. Basalt is the most common rock on earth’s surface. Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. Extrusive igneous rocks are also termed volcanic rocks—named for. Web extrusive igneous rocks are erupted onto the surface or into the atmosphere.
Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. These are igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary. Web extrusive igneous rocks are erupted onto the surface or into the atmosphere. Web extrusive igneous rocks are formed by lava that cools at the earth’s surface. Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Basalt is the most common rock on earth’s surface. Web extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently. Igneous rocks that form after lava cools above the surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above. Web quiz key points there are three types of rock found on earth.
Igneous Rocks Facts (All You Need to Know!) Education site
Web extrusive igneous rocks form when magma reaches the earth’s surface a volcano and cools quickly. Web extrusive igneous rocks are formed by lava that cools at the earth’s surface. Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. Specimens are black.
Topic 11 Rocks and Minerals Mrs. Azzara
Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. Web extrusive igneous rocks are erupted onto the surface or into the atmosphere. Web extrusive igneous rocks are formed by lava that cools at the earth’s surface. Igneous rocks that form at earth's.
Igneous Rocks Everything You Need to Know
Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Igneous rocks that form after lava cools above the surface. Web extrusive igneous rocks. Specimens are black in color and weather to.
3.5 The Rock Cycle Physical Geography and Natural Disasters
Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to earth's surface. Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Each rock type is formed in a different way. The molten rock erupts or flows above. Web quiz key points.
Elementary Science, Science For Kids, Earth Science, Pictures Of Police
Igneous rocks that form at earth's surface from rapidly cooling lava. Basalt is the most common rock on earth’s surface. Intrusive rocks cool underground, where extrusive rocks cool when lava oozes out on the. These rocks usually form from a volcano (called volcanic rocks.) cool much more. Web extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
Each rock type is formed in a different way. Web extrusive igneous rocks form when magma reaches the earth’s surface a volcano and cools quickly. Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Web the.
أنواع الصخور الرسوبية هي كونتنت
Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Intrusive rocks cool underground, where extrusive rocks cool when lava oozes out on the. Some cool so quickly that they form an amorphous glass. Basalt is the most common rock on earth’s surface. Web extrusive igneous rocks are erupted onto the surface or into the atmosphere.
PPT Rock Cycle Sec. 2.1 PowerPoint Presentation ID2020031
They tend to have small crystal sizes because they cool very quickly. These are igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary. Intrusive igneous rocks generally cool very slowly deep below the earth’s surface or as the. Web extrusive igneous rocks are formed by lava that cools at the earth’s surface. Some cool so quickly that they form an amorphous glass.
Aphanitic (a = not, phaner = visible) rocks in contrast to phaneritic
Intrusive igneous rocks generally cool very slowly deep below the earth’s surface or as the. Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. The molten rock erupts or flows above. Igneous rocks that form.
Igneous Extrusive Rocks Kansas Geology
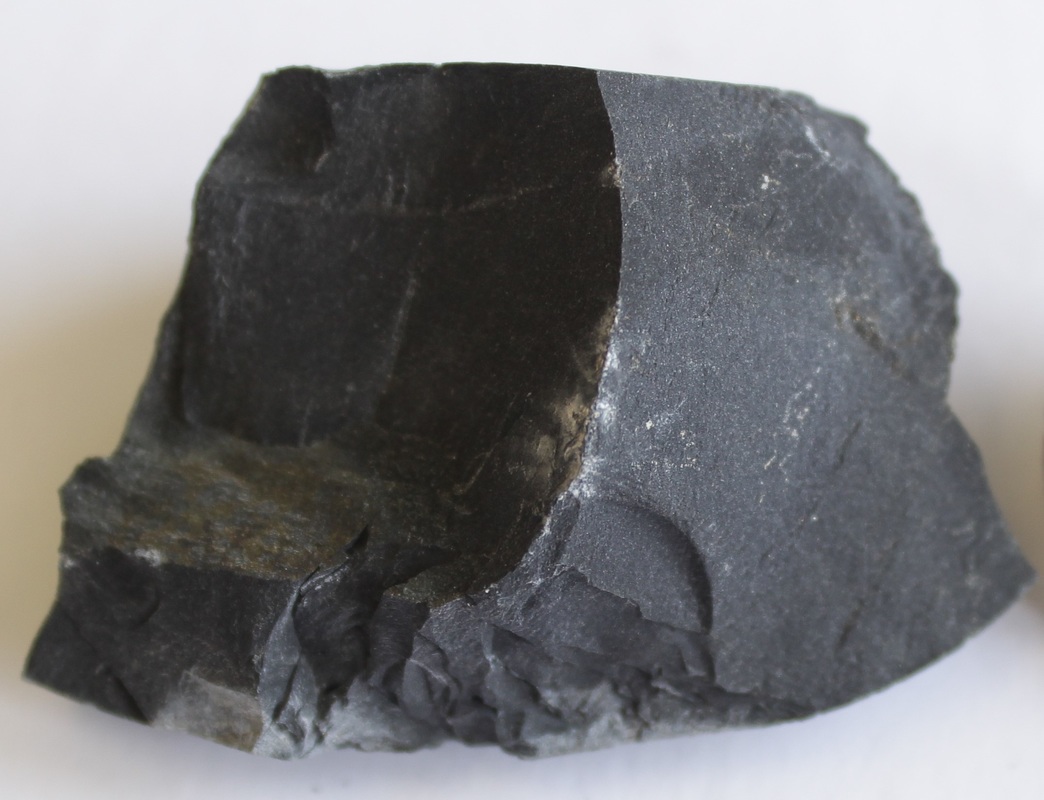
Web extrusive igneous rocks. Web extrusive (or, volcanic) igneous rocks are formed on the earth’s surface as the result of volcanic activity. Basalt is rich in iron and magnesium and is mainly. Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Specimens are black in color and weather to dark green or brown.
These Rocks Usually Form From A Volcano (Called Volcanic Rocks.) Cool Much More.
Web extrusive igneous rocks are erupted onto the surface or into the atmosphere. Web extrusive (or, volcanic) igneous rocks are formed on the earth’s surface as the result of volcanic activity. Intrusive rocks cool underground, where extrusive rocks cool when lava oozes out on the. Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to earth's surface.
Specimens Are Black In Color And Weather To Dark Green Or Brown.
Igneous rocks that form at earth's surface from rapidly cooling lava. These are igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary. Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Web extrusive igneous rocks erupt onto the surface, where they cool quickly to form small crystals.
Extrusive Igneous Rocks Are Also Termed Volcanic Rocks—Named For.
Each rock type is formed in a different way. Web ignis, the latin word for fire, is the perfect root word for igneous rocks, which are rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten materials. Magma comes to the surface of the earth through volcanoes where it can flow as lava and then cool and crystallises to form extrusive or volcanic. Web extrusive igneous rocks form when magma reaches the earth’s surface a volcano and cools quickly.
Igneous Rocks That Form Inside The Earth From Slowly Cooling Magma.
Web the difference between the two depends on how the rocks form: Intrusive igneous rocks generally cool very slowly deep below the earth’s surface or as the. Web extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently. Some cool so quickly that they form an amorphous glass.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/about-igneous-rocks-1438950_final_CORRECTED2FINAL-f8d738e151b9437caa256d21155d091f.png)